What Makes a Successful Software Company? Delivering high-quality products! Imagine the embarrassment of providing a project that does not function properly or is full of bugs. That’s why testing plays a crucial role.
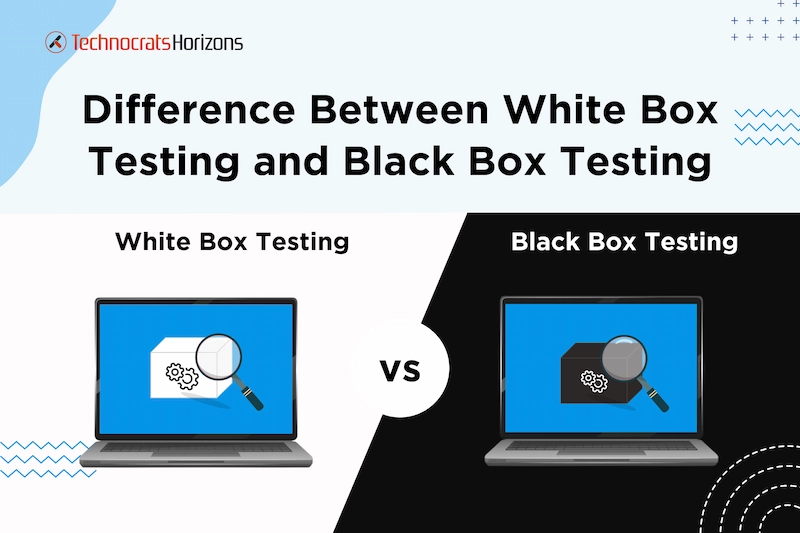
But testing is not so one-dimensional; there are different types of tests that serve various purposes. The most known and significant testing methods are white box and black box testing.
In this blog post, we will concentrate on understanding the key differences between white box and black box testing. To begin, let’s provide a brief overview of testing methods commonly used in software development. We will explore black box vs. white box testing and how they differ from each other under different criteria.
What is White Box Testing?
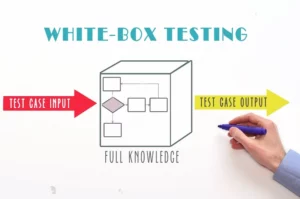
White box testing is a software testing method that involves examining the inner workings of your system, including its code, structure, logic, and architecture. To effectively utilize this testing technique, the tester must possess a strong understanding of coding. Typically, this method is employed by developers who have full access to the system’s source code during the testing process.
Pros:
-
- Provides comprehensive coverage of code paths, ensuring thorough testing.
- Allows for early detection and resolution of code-level issues.
- Offers detailed debugging capabilities, aiding in pinpointing problems.
- Efficient for unit and integration testing, speeding up development.
- Validates internal logic and algorithms, ensuring correctness.
Cons:
-
- Requires programming knowledge, limiting accessibility.
- Can be time-consuming for complex systems, potentially delaying testing.
- May miss high-level or integration issues, focusing primarily on internals.
- Limited in assessing user experience, neglecting external behavior.
- Tests may not reflect real-world usage, potentially overlooking critical scenarios.
What is Black Box Testing?
Black box testing assesses whether a system complies with business requirements and meets end-user expectations, without considering its programming or internal workings. Testers test the software’s input and output by providing inputs at the user interface (UI) level and evaluating whether the resulting output meets the actual needs. They conduct this test on the application’s user interface because they do not have access to the source code.
Pros:
-
- Mimics real-world user interactions, providing a realistic assessment.
- Validates against functional requirements, ensuring the software meets specifications.
- Doesn’t require knowledge of code internals.
- Efficient for system and acceptance testing, contributing to quicker results.
- Identifies usability and performance issues, improving user satisfaction.
Cons:
-
- Offers limited visibility into code issues, potentially missing internal defects.
- May overlook certain internal problems, as it focuses externally.
- Less effective for complex algorithms, especially without code visibility.
- Test coverage can be challenging to measure accurately.
- Relies on predefined test cases and scenarios, potentially missing unforeseen issues.
White Box vs. Black Box Testing: How to Perform
-
-
White Box Testing
-
Unit Testing: Software developers commonly use unit tests to validate specific sections of code or components within an application. Developers typically create unit tests that execute the code with predefined inputs to identify errors and ensure that the code operates as intended. Unit tests can also be valuable for assessing complex algorithms and helping developers pinpoint minor issues in the code. In most cases, unit tests are executed during the build process.
Integration Testing: Integration testing involves verifying that separate components function correctly when combined. The goal is to uncover any discrepancies in interfaces and interactions that could lead to software malfunctions.
-
-
Black Box Testing
-
Effective black box testing requires careful planning, making it essential to have a skilled Quality Assurance specialist who can assist with the following steps:
Test Case Execution: After completing the above-mentioned steps, a quality assurance specialist should execute test cases, thoroughly analyze the data, identify any issues that arise, and then retest everything once the errors have been fixed.
It may seem like a lot of work, but the primary goal of all these activities is to compare the product to the established criteria. If any discrepancies are detected, every team member involved in the project will be notified and can make the necessary corrections more efficiently and quickly. We all recognize the importance of saving both time and money whenever possible.
Need High-Quality Custom Web Development? Choose Us!!
White Box vs. Black Box Testing: When You Need Them
-
-
White Box Testing
-
It is a technique used to examine the control and data flow within the code, allowing us to evaluate the internal structure and architecture of a software system. This testing approach can be applied at various stages of the software development life cycle, including requirements analysis, design, and test case preparation. It is typically utilized in the earlier phases of system development, such as unit, system, and integration testing.
By incorporating white box testing throughout the development cycle, we can create a more robust, dependable, and higher-quality software system that meets the needs of its intended users.
Automated testing plays a significant role in testing complex algorithms. For example, automated tests can be employed to ensure the accuracy of results from intricate pieces of code. Integration testing usually marks the final testing phase before the release of a finished product.
-
-
Black Box Testing
-
Black box testing is a vital step in the software development process that begins early in a project’s life cycle. It is consistently applied throughout the project to evaluate the program’s functionality and external behavior, aligning it with end-user requirements.
To ensure the effectiveness of this testing strategy, testers should actively participate in requirements collection and analysis. This involvement allows them to gain a comprehensive understanding of the client’s needs and ensures the thoroughness of the testing process. Additionally, testers should take an active role in creating and preparing test data and scenarios as the design phase progresses. Testers use methods like error guessing, equivalence partitioning, and boundary value analysis for test cases.
The proactive nature of black box testing facilitates the early identification and correction of flaws in the development process. This, in turn, enhances the final product’s quality and reliability.
White Box vs. Black Box Testing: Process
-
-
White Box Testing
-
In comparison to black box testing, the white box testing procedure is more focused. It is applied to smaller components of vital functionality, parts, and applications, making it highly effective.
This procedure employs an explanatory flowchart to ensure flawless execution in the end. The process begins with identifying the target, followed by creating a flowchart and addressing any flaws.
-
-
Black Box Testing
-
On the other hand, black box testing requires a thorough examination of a specific application, with the primary goal of delivering a high-quality experience to end users.
When bugs are discovered, they are reported to the development team for resolution.
Critical to this software testing process is the comparison of actual results with expected ones. Any tests that fail are classified as flaws or bugs.
White Box vs. Black Box Testing
Below is the list of major differences between white box testing and black box testing based on different parameters:
| S. No. | Parameter | White Box Testing | Black Box Testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Basic | White Box Testing examines internal code. | Black Box Testing focuses on external functionality. |
| 2 | Objective | It evaluates internal logic and paths. | Validates against requirements. |
| 3 | Programming Knowledge | It requires considerable coding knowledge. | It requires minimal coding knowledge. |
| 4 | Automation | It is easily automated. | It can be automated but requires effort. |
| 5 | Testing Method | It is a form of structural testing. | It encompasses functional and non-functional testing. |
| 6 | Tested By | It is typically conducted by developers and testers. | It is carried out by independent testers or QA teams. |
| 7 | Time | Time-consuming due to code examination. | Time-efficient, focusing on functionality. |
| 8 | Implementation Knowledge | Demands an in-depth understanding of the system’s internals. | Requires minimal knowledge of the system’s internals. |
| 9 | Benefit | It excels at thorough bug detection, especially within the code. | It offers real-world user experience testing. |
| 10 | Types | Techniques like Statement coverage, and path coverage. | Functional, non-functional, etc. |
| 11 | Drawbacks | It may miss integration issues due to its internal focus. | It has limited visibility of code issues. |
| 12 | Examples | Reviewing and testing the code that calculates interest rates in a banking software application. | Testing the registration process on a website to ensure users can sign up without delving into the code. |
Conclusion
This blog post discussed the major distinctions between black box testing and white box testing. Both testing methods have their advantages and limitations, and they excel in specific testing scenarios. Whether used independently or in combination, they are capable of identifying issues and improving the overall quality of the system.
Did this article clarify the key differences between white box vs. black box testing? Let us know on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn!
We Find Bugs Before Users Do!! Hire Us Now!!
Need a unique web solution?
Our experts are here to build you results-driven custom web solutions.






 Request a
Request a